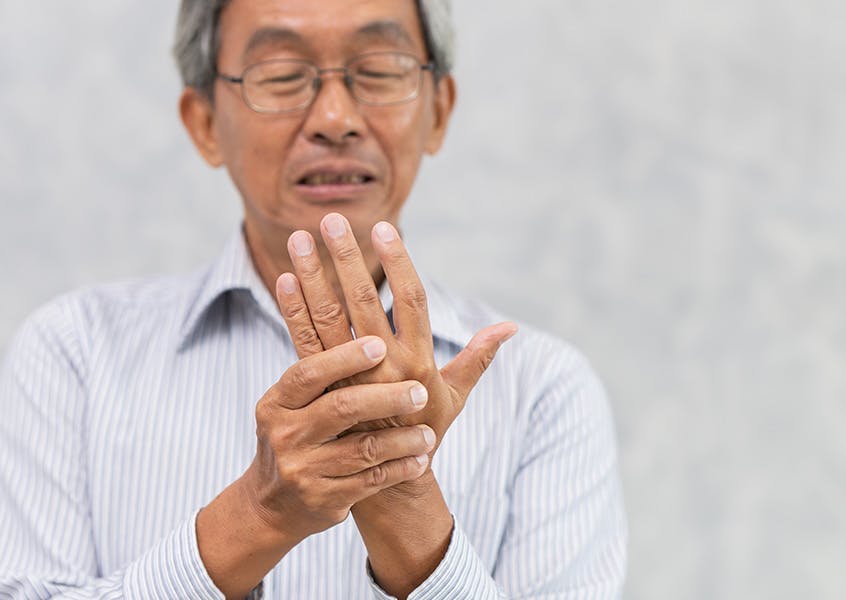
Parkinson's Disease is a neurodegenerative condition that primarily affects the elderly, caused by the natural deterioration of the body's system, resulting in hand tremors and other symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. If left untreated, the disease can lead to coordination difficulties, muscle stiffness, speech and swallowing problems, and balance issues. It is crucial to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those with Parkinson's disease. Read on to learn more about the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of Parkinson's disease.
Understanding the Causes of Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a prevalent neurodegenerative disease that commonly affects the elderly and is often associated with Alzheimer's disease. It is a slowly progressive condition that affects the nervous system responsible for producing the neurotransmitter dopamine in the midbrain. When dopamine levels are reduced due to the death of that part of the brain, it can lead to movement disorders, the most apparent manifestation of which is hand tremors.
Patients with Parkinson's disease can be divided into two groups: those with "real" Parkinson's disease and those with Parkinsonism-plus syndromes. The former is not curable, while the latter has a cure, as the cause of the disease is related to medication, dizziness, sleeping pills, ischemic stroke, depletion of the brain, hypothyroidism, or other underlying conditions that result in Parkinsonism. If you suspect you or someone you know may have Parkinson's disease or Parkinsonism, it is essential to seek a professional diagnosis from a doctor. Read on to learn more about Parkinson's disease and how it can be managed.
Warning Signs of Parkinson's Disease
Abnormal symptoms in patients begin to manifest after brain cells start to die, which can take 4-10 years. The following symptoms may be observed:
1. Tremors – slight shaking in fingers, wrists, or chin when at rest or not paying attention.
Similar symptoms in normal people – hand tremors can be caused by exercise, stress, anxiety, certain medications, or age-related joint and vision problems.
2. Writing smaller letters – changes in handwriting, such as smaller letters or spacing.
Similar symptoms in normal people – age-related joint and vision problems.
3. Loss of smell or taste – decreased sense of smell for certain foods or fruits.
Similar symptoms in normal people – loss of smell and taste during cold or fever, but it returns to normal after recovery.
4. Difficulty sleeping – sleepwalking or gesturing during sleep, noticeable from bruises.
Similar symptoms in normal people – normal people may sleepwalk but with less severity.
5. Difficulty moving or walking – feeling stuck or arms swinging unequally.
Similar symptoms in normal people – may occur in those who have had joint injuries.
6. Constipation – one of the first symptoms in some Parkinson's patients.
Similar symptoms in normal people – insufficient fiber intake or certain medications can cause constipation.
7. Soft or slurred speech
Similar symptoms in normal people – can occur during cold or respiratory viral infections, and it returns to normal after recovery.
8. Facial expression shows no emotion
Similar symptoms in normal people – can be a side effect of certain medications, but it will recover when the drug is stopped.
9. Dizziness or fainting – feeling lightheaded when changing posture due to low blood pressure.
Similar symptoms in normal people – can be caused by fatigue or certain drugs.
10. Stooped or arched back – unable to straighten up properly.
Similar symptoms in normal people – can be caused by injuries or pain in the abdomen, joints, or spine.
Parkinson's Disease Symptoms
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease can be classified into two categories: motor symptoms and non-motor symptoms.
· Motor symptoms include four main symptoms:
§ Tremor in hands, legs or chin which usually occurs at rest when not using that part;
§ Rigidity which is often detected by a doctor and usually occurs on arms, legs, neck, or trunk;
§ Bradykinesia, in which the patient's movements are slow, and the amplitude of movement gradually decreases, with a feeling of difficulty in moving the body, usually on one side first
§ Postural instability, in which the patient may fall more easily than usual with the body and head leaning forward.
· Non-motor symptoms can be divided into 5 major groups:
§ Sleep disorders such as snoring, insomnia, daytime sleepiness, sleepwalking fight;
§ Autonomic dysfunctions such as urinary incontinence, difficulty urinating, constipation, erectile dysfunction in men, and fainting when changing positions;
§ Mood-behavior-cognitive impairments, such as depressed mood and anxiety, which can be found in the early stages of the disease. Meanwhile, disabilities in thinking and decision-making are often seen in the later stages of the disease;
§ Hyposmia / Anosmia can be present before the movement is abnormal
§ Problems with pain, numbness, or fatigue, limb muscles may occur either during the time the Parkinson's disease medication has worn off or during the time the medication is working.
Preliminary Parkinson's Examination with 11 Questions
To help individuals assess whether they may have Parkinson's disease, we have created an initial checklist consisting of 11 questions. This checklist is intended for individuals who may be experiencing symptoms and want to evaluate their risk before seeking medical advice. The 11 questions are as follows:
1. Have you ever experienced tremors in your hands or legs?
2. Do you have difficulty standing up from a chair?
3. Do you take short, shuffling steps when you walk?
4. Do your arms swing less when you walk?
5. Does your back hunch over when you walk?
6. Do you have trouble turning around when walking?
7. Has your voice become softer or weaker than before?
8. Do you struggle to turn over in bed while sleeping?
9. Do you write smaller or slower than before?
10. Have you noticed a slower pace in daily activities such as dressing, showering, or combing hair?
11. Do you have trouble snapping buttons or opening water bottles?
By answering these questions, individuals may be able to identify certain symptoms that are commonly associated with Parkinson's disease. However, it is important to note that only a medical professional can make an accurate diagnosis. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about your health, it is best to speak with your doctor.
Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis
In order to distinguish between Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonism-plus syndromes, the physician will conduct a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. Following this initial evaluation, the patient will undergo a more detailed assessment that may include a CT scan or MRI, as well as an F-DOPA PET scan. These imaging tests can detect any irregularities in dopamine levels in the brain, helping to confirm a Parkinson's disease diagnosis and rule out other potential conditions.
Guidelines for Treating Parkinson's Disease
The following are the recommended approaches for treating Parkinson's Disease:
1. Drug therapy: Medications can be prescribed to enhance dopamine activity in the brain, resulting in improved muscle control and more fluid movements. It is important to note that while drug therapy can help alleviate symptoms, it cannot reverse the degeneration of brain cells.
2. Surgical treatment: In certain cases, deep brain stimulation may be recommended to improve the patient's symptoms.
3. Exercise and physical therapy: Exercise and physical therapy can be utilized to improve overall fitness levels and enhance mobility. Activities such as walking, cycling, dancing, and tai chi are beneficial for individuals with Parkinson's Disease. These types of exercises can help manage symptoms, improve balance, and increase overall quality of life.
Parkinson's disease is a condition that predominantly affects the elderly population, causing significant disruptions to their daily lives. While it may not be life-threatening, it can still have a profound impact on individuals and their loved ones. As such, it's essential to keep a lookout for any abnormal symptoms in your family members. If you notice any warning signs, it's important to consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
For Krungthai-AXA customers who have Surgical Life Insurance, you can get additional advice from Krungthai-AXA service. For more information about your treatment decision, see more details at: https://www.krungthai-axa.co.th/th/care-coordination.
References
· Sikarin Hospital
· Bumrungrad Hospital
· Siriraj Hospital
· Ramkhamhaeng Hospital
· Bangkok Hospital
· Phyathai Hospital
· Synphaet Hospital